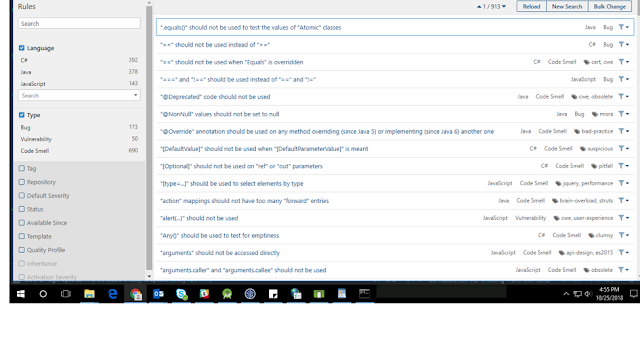
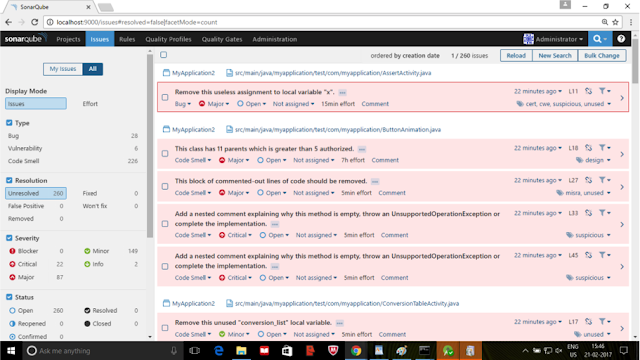
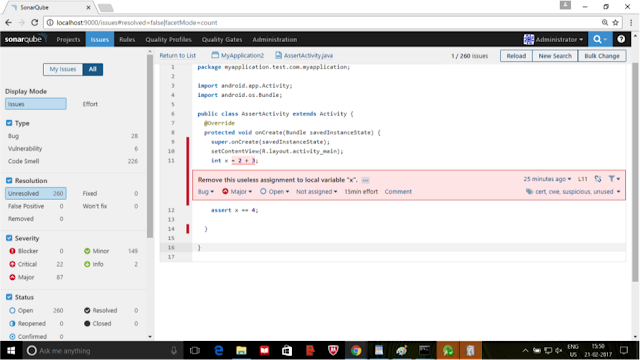
If you go through previous section Part 1: Travis CI introduction that would be helpful to follow my steps from this article.
Step 1 : Creating a user authentication token for your account on SonarCloud
If we want to enforce security by not providing credentials of a real SonarCloud user to run your code scan, we have to provide a User Token as a replacement of the user login. This will increase the security of your installation by not letting your analysis user's password going through your network.

The easiest way to encrypt Sonar token with the public key is to use Travis CLI. This tool is written in Ruby and published as a gem. Please follow the link Install gem
Note : I suggest to use mac system to install gem if possible that would be easy to install & generate key.
travis encrypt SONAR_TOKEN
The above command generates encrypted Sonar token to use in travis.yml file
Step 2 : Encrypting generated Sonar token
The easiest way to encrypt Sonar token with the public key is to use Travis CLI. This tool is written in Ruby and published as a gem. Please follow the link Install gem
Note : I suggest to use mac system to install gem if possible that would be easy to install & generate key.
travis encrypt SONAR_TOKEN
The above command generates encrypted Sonar token to use in travis.yml file
Step 3: Get SonarCloud.io Organization
you want to push your project on and get its key

Step 4 :
We have to create a sonar-project.properties file to the root folder of Android application.
sonar.projectKey=Same project key from the SonarCloud project
sonar.projectVersion=1.0
sonar.host.url=https://sonarcloud.io
sonar.projectKey=Same project key from the SonarCloud project
sonar.projectVersion=1.0
sonar.host.url=https://sonarcloud.io
sonar.organization=organization key from SonarCloud
sonar.projectName=Same project name from the SonarCloud project
sonar.login= SonarCloud Username
sonar.password= SonarCloud Password
# =====================================================
# Meta-data for the project
# =====================================================
sonar.sourceEncoding=UTF-8
sonar.sources=src/main/java
sonar.java.binaries=build
sonar.binaries=build
sonar.language=java
sonar.profile=Android Lint
Step 5:
Add the following lines to your .travis.yml file to trigger the analysis.
Whenever user pushed to the specified branch in yml file, the sonar analysis triggers & generates measure data in “https://sonarcloud.io/”
Please feel free to share your queries.
Happy coding !!!